Volkswagen introduces dual SCR technology on diesel cars
4 September 2019
Volkswagen has introduced a dual SCR catalyst configuration on diesel vehicles, which enables meeting the Euro 6d (2020/2021 for new types/all vehicles) emission standards. The new aftertreatment configuration, dubbed “twin-dosing”, was first used in the updated 2019 Passat 2.0 TDI Evo with 110 kW (150 PS) power output. Volkswagen intends to gradually introduce the dual SCR technology to all models with 2.0 TDI Evo engines, including the coming new VW Golf in all its TDI variants.
In RDE (real driving emissions) measurements, NOx emissions from the new 2.0 TDI Evo with dual SCR were reduced by around 80% compared to the previous generation of the vehicle, according to Volkswagen.
Compared to the earlier configuration, the new aftertreatment system includes a second SCR catalytic converter which is located in the underbody of the vehicle, followed by an ammonia oxidation catalyst (ASC). As the exhaust temperature in the underfloor position can be as much as 100°C lower than that close to the engine, this expands the temperature window for the SCR system—even at exhaust gas temperatures close to the engine of +500°C, the system is still able to achieve very high conversion rates, Volkswagen said.
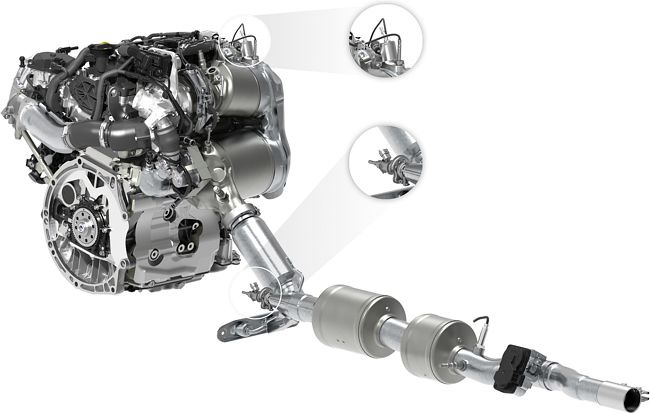
In the earlier configuration, only one, close-coupled SCR catalyst was used—applied onto the diesel particulate filter (SCRF)—and positioned downstream of the turbocharger and a diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC). In this close-coupled arrangement, the exhaust gas temperatures required for high conversion rates can be achieved quickly after a cold start—the ideal range for conversion rates of more than 90% is between +220°C and +350°C.
Thanks to the second, underfloor SCR catalyst, the new system can maintain high NOx conversion rates above +350°C as well. Temperatures at this level occur for example when driving at high speeds on the motorway, at high engine speeds over prolonged periods of time and when driving uphill, especially if the vehicle is fully loaded or towing a trailer.
Since 2018, VW has been using only SCR technology on models with diesel engines. Earlier, NOx adsorbers rather than SCR were used on smaller size engines, including many models involved in the diesel emission scandal.
Dual SCR configurations with an added close-coupled SCR catalyst—to address cold start/low temperature NOx emissions—are being considered for future heavy-duty diesel engines, both in North America and in the European market.
Source: Volkswagen